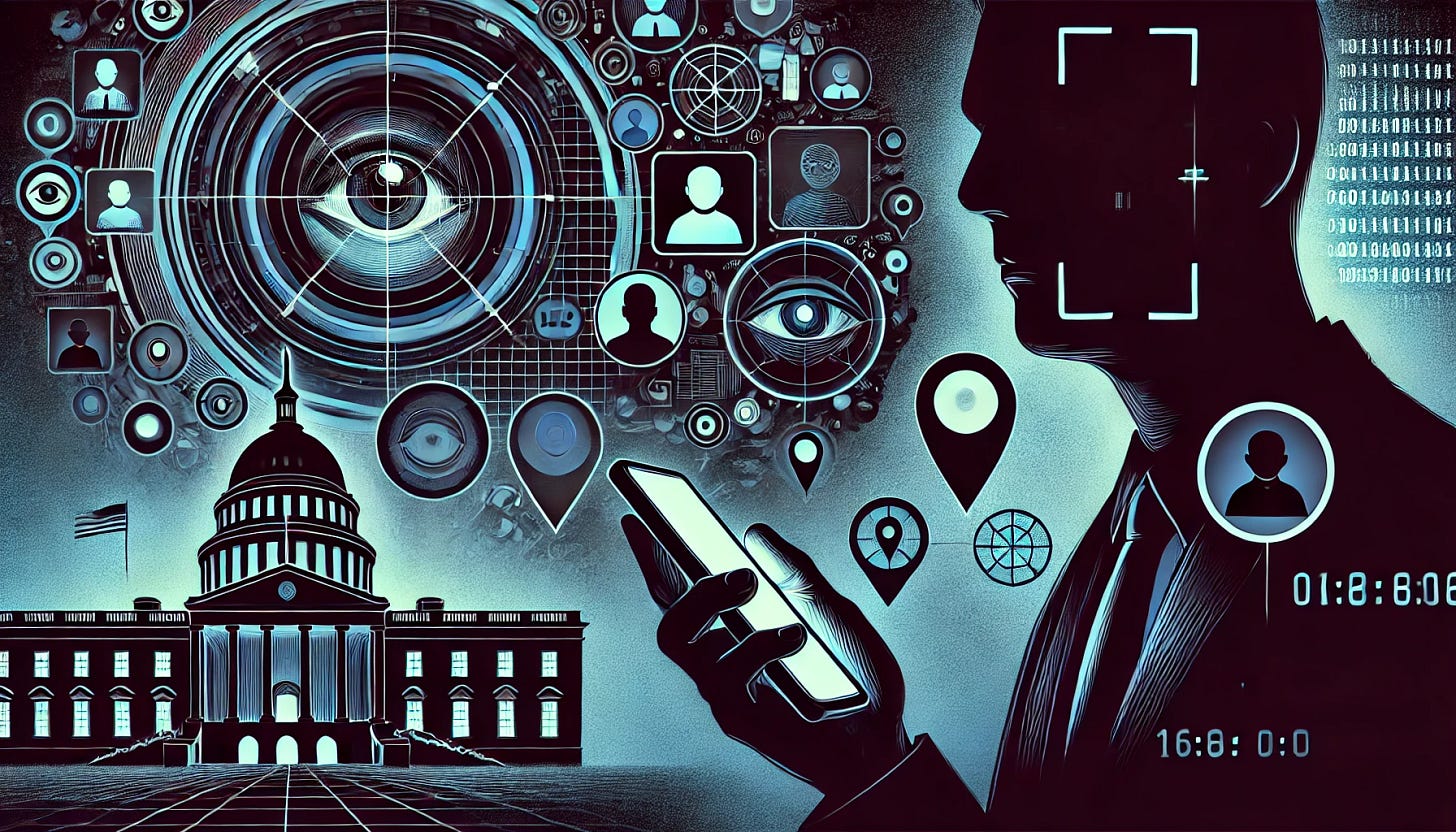
With Donald Trump’s recent election victory, new concerns are rising about the future of privacy in America. Trump has announced policies aimed at mass deportation, enhanced monitoring of political opponents, and a hardline stance on immigration. These goals are expected to rely heavily on AI-driven surveillance systems—meaning the technology of facial recognition, predictive analytics, and digital tracking could expand significantly in the U.S.
This issue dives into how AI-powered government surveillance may be used in the coming months and the steps you can take to protect your data and privacy.
Trump’s Agenda and the Role of AI Surveillance
Trump’s plans include:
Mass Deportations: Trump has pledged the largest deportation campaign in U.S. history. AI technology could expedite these efforts by analyzing location data, biometric information, and social connections to identify and monitor individuals.
Political Surveillance: Given Trump’s history of criticizing journalists and activists, AI could be leveraged to track dissidents or opponents by scanning social media, analyzing sentiment, and monitoring public gatherings.
Targeting of Specific Communities: Predictive analytics might be used to target high-density immigrant communities or flag individuals based on connections or digital behavior, possibly leading to profiling and undue targeting.
AI Tools that Power Government Surveillance
In Trump’s enforcement-driven vision, several AI tools stand out:
Sentiment Analysis: AI algorithms can scan social media and communications to detect dissenting opinions or track keywords. This could serve to identify political opponents or those expressing opposition to policies.
Predictive Analytics in Immigration Enforcement: AI can analyze movement patterns, associations, and even financial transactions to locate or predict the locations of undocumented immigrants, potentially leading to disproportionate enforcement in certain areas.
Countermeasures: Protecting Your Privacy in the Age of AI Surveillance
To reduce exposure to AI surveillance tools, privacy advocates recommend:
Use Encrypted Communication: End-to-end encrypted messaging apps like Signal ensure that only you and the recipient can read messages, making it harder for third parties to access private communications.
Minimize Location Tracking: Limit location services on your smartphone, and use privacy-focused browsers like Tor to obscure your online location. These steps help reduce the digital “footprint” available to tracking algorithms.
AI-Powered Anonymity Tools: Tools that use AI to mask metadata or scramble facial features in photos can limit surveillance reach. Noise-injection algorithms, for instance, add subtle “noise” to images, making it more difficult for facial recognition to identify individuals.
The Ethical Implications of AI Surveillance
As Trump’s administration prepares to expand AI’s role in surveillance, ethical questions around transparency, accountability, and bias become more pressing:
Bias and Profiling Risks: Facial recognition and predictive models can contain biases that disproportionately affect marginalized groups, potentially leading to profiling and discrimination in targeted communities.
Lack of Transparency: AI models often operate as “black boxes” where decisions are made without clear explanations. As surveillance systems grow, it becomes harder for citizens to understand how and why they might be targeted.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Civil Liberties in a Surveillance Era
In this climate, it’s crucial to stay informed about how AI impacts surveillance and privacy rights. AI’s dual nature—as both a tool of surveillance and a protector of privacy—means we must balance convenience with an understanding of potential risks. As privacy-conscious individuals, we can take proactive steps to protect our data and support responsible, fair applications of AI technology in government.
I'm a retired educator and freelance writer who loves researching AI and sharing what I've learned.
Vocabulary Key
Facial Recognition: AI technology that identifies individuals by analyzing unique facial features. Commonly used in security and surveillance.
Sentiment Analysis: AI technique that interprets emotional tone from text data, such as social media posts or messages.
Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms that analyze data to make predictions about future behaviors or trends.
End-to-End Encryption: A form of data protection where only the communicating users can read the messages, preventing third-party access.
Black Box: A model or system where the processes are not visible or explainable, making it difficult to understand how outputs are generated from inputs.
FAQs
How could the Trump administration use AI in its policies? The administration could use AI for deportations, monitoring political dissent, and tracking individuals by scanning location data, analyzing online behaviors, and predicting associations.
What are the main AI tools involved in government surveillance? Facial recognition, sentiment analysis, and predictive analytics are some of the main tools likely to be used.
How can I protect my data and communications? Using encrypted messaging apps, disabling location services, and using privacy-focused browsers like Tor are good steps for protecting your digital privacy.
What are the ethical concerns with AI-driven surveillance? Key issues include bias, lack of transparency, and potential overreach, all of which could lead to privacy invasions and profiling.
Can AI be used to protect privacy as well as enforce surveillance? Yes, AI can also help protect privacy through tools like encryption, noise injection, and anonymizing features, providing countermeasures to surveillance.
#Trump2024 #AISurveillance #DigitalPrivacy #AIinGovernment #PredictivePolicing #DeepLearningDaily #FacialRecognition #PrivacyProtection #AIethics #Encryption














Share this post